The harmonic wave yi = (2 x 10^-3)cos pi(2x - 50t) travels along a string toward a boundary at x = 0 with a second string. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
The harmonic wave yi = (2 x 10^-3)cos pi(2x - 50t) travels along a string toward a boundary at x = 0 with a second string. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
24.19. The equation of a simple harmonic wave is given byy 3in (50t x), where x and y are in metresand t is in seconds. The ratio of maximum particle2velocity to the
![SOLVED: matlab plllllz Question1[5marks]: Import the audio file found on CMS noise=0.1*cos(2*pi*50*ID*t Add noise to the first half of the audio signal Hint:Don't forget to start your script with clear all close SOLVED: matlab plllllz Question1[5marks]: Import the audio file found on CMS noise=0.1*cos(2*pi*50*ID*t Add noise to the first half of the audio signal Hint:Don't forget to start your script with clear all close](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/69b702c98e304501bb53b3ef8abca285.jpg)




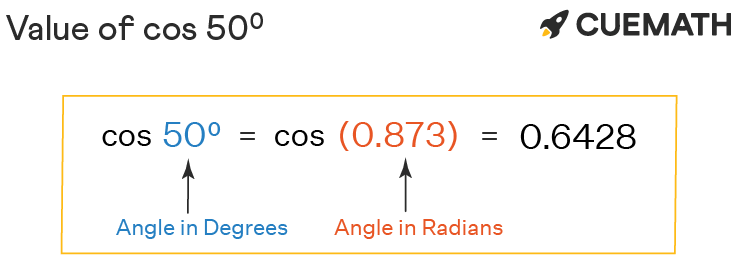




![The value of sec [ sin ^-1 [ - sin50pi/9 ] + cos ^-1cos [ - 31pi/9 ] ] is equal to - The value of sec [ sin ^-1 [ - sin50pi/9 ] + cos ^-1cos [ - 31pi/9 ] ] is equal to -](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m3TyMCMQy0c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Inverse Fourier Transform of | cos[(2 pi f)/100)] | - Mathematics Stack Exchange Inverse Fourier Transform of | cos[(2 pi f)/100)] | - Mathematics Stack Exchange](https://i.stack.imgur.com/IIZ5d.jpg)

