Interesting approach proof sum 1/n^4= pi^4/90. No Fourier expansion, no Taylor series. No calculus - YouTube

sequences and series - Using roots of unity to prove that $\cos\frac{\pi }{2n}\cos\frac{2\pi}{2n}\cdots\cos\frac{(n-1)\pi}{2n}=\frac{\sqrt{n}}{2^{n-1}}$ - Mathematics Stack Exchange
![Prove that sum(r=0)^n^n Cr(-1)^r[i+i^(2r)+i^(3r)+i^(4r)]=2^n+2^(n/2+1)cos(npi//4),w h e r ei=sqrt(-1)dot Prove that sum(r=0)^n^n Cr(-1)^r[i+i^(2r)+i^(3r)+i^(4r)]=2^n+2^(n/2+1)cos(npi//4),w h e r ei=sqrt(-1)dot](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/web-thumb/32132_web.png)
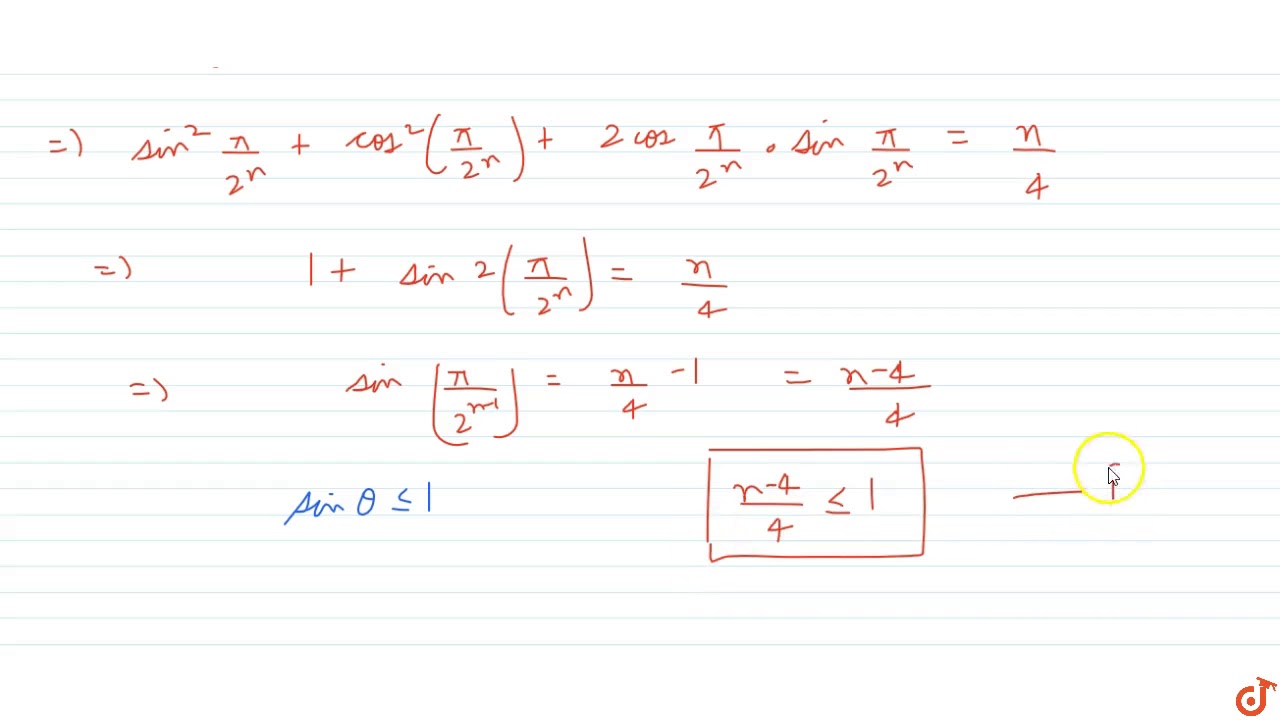
Prove that sum(r=0)^n^n Cr(-1)^r[i+i^(2r)+i^(3r)+i^(4r)]=2^n+2^(n/2+1)cos(npi//4),w h e r ei=sqrt(-1)dot

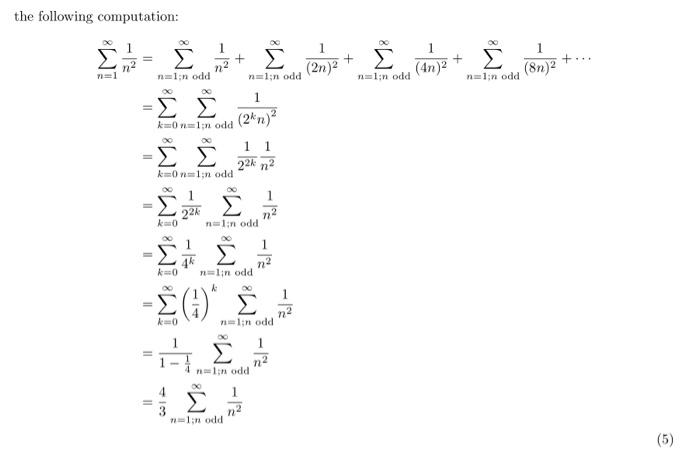
Ankur Handa on Twitter: "@InertialObservr If you plug t = 1/pi in the last two equations you arrive at the result. This one extends from the Basel problem also used to obtain

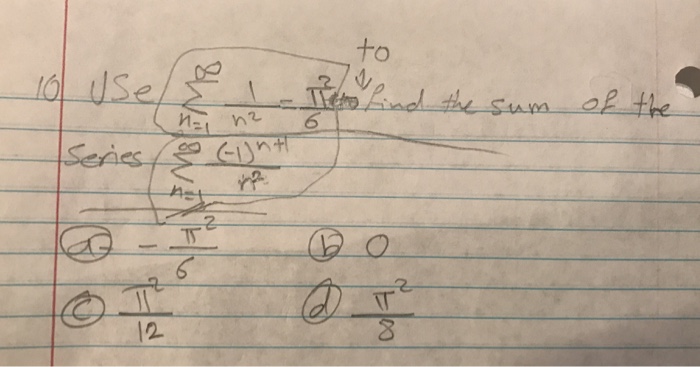
Given that `sum_(n=1)^oo 1/n^2=pi^2/6 and sum_(n=1)^oo 1/(n^2+8n+16)=pi^2/a-b` where a in `N ... - YouTube