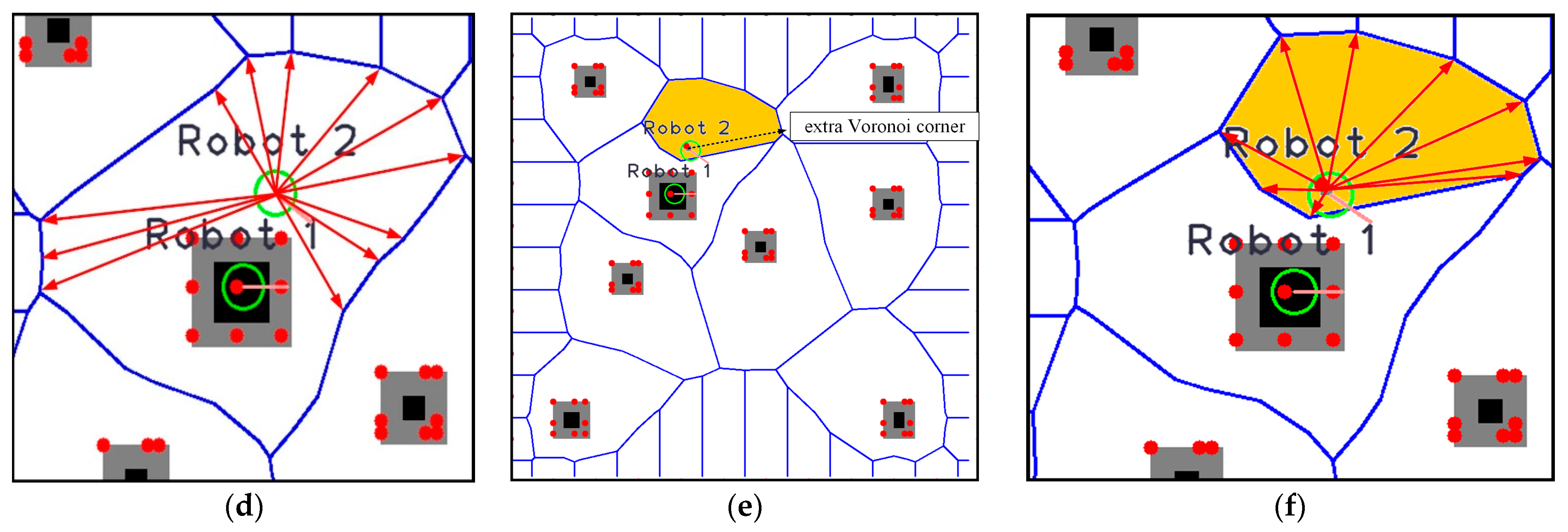
Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A Path Planning Strategy for Multi-Robot Moving with Path-Priority Order Based on a Generalized Voronoi Diagram

Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A Path Planning Strategy for Multi-Robot Moving with Path-Priority Order Based on a Generalized Voronoi Diagram

Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A Path Planning Strategy for Multi-Robot Moving with Path-Priority Order Based on a Generalized Voronoi Diagram

Path of SocBot robot moving to a target point at 0.4ms −1 and simulated... | Download Scientific Diagram
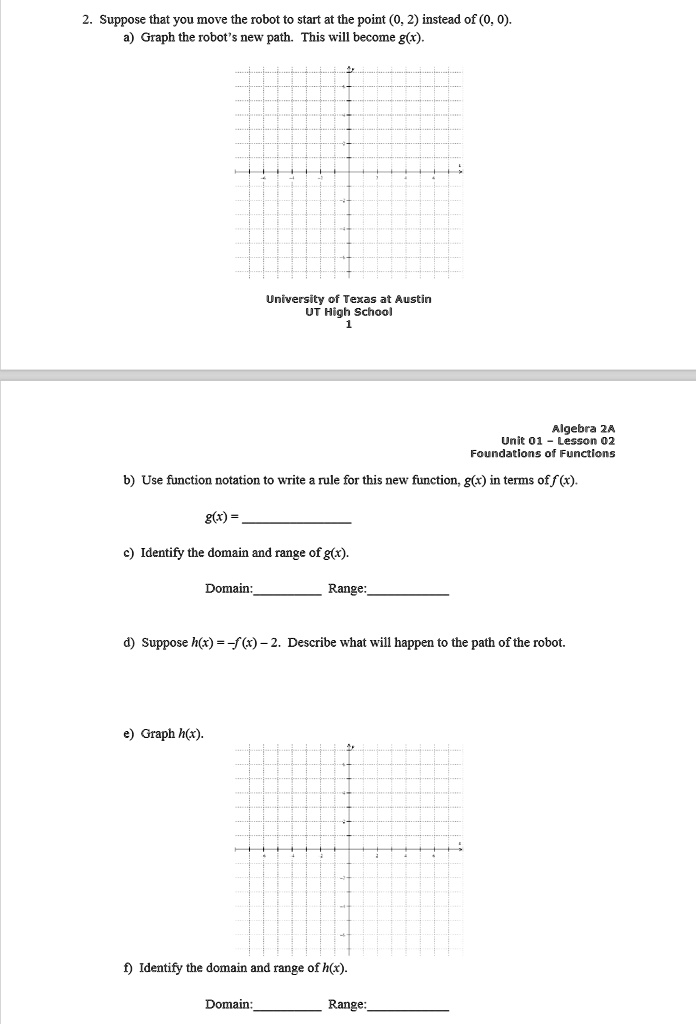
SOLVED: 2. Suppose that you move the robot to start at the point (0, 2) instead of (0, 0). Graph the robot' = new path: This will become g(r). University of Texas

Chapter 5 Trajectory Planning 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapters ……. Path and trajectory planning means the way that a robot is moved from one location. - ppt download
3 Questions: How the MIT mini cheetah learns to run | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology

a) The robot moves on the stimulation point following a minimum jerk... | Download Scientific Diagram



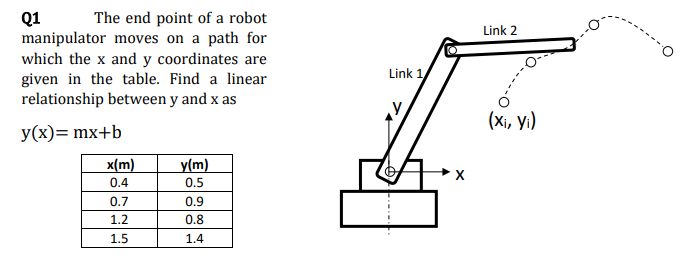



![PDF] Minimum cost trajectory planning for industrial robots | Semantic Scholar PDF] Minimum cost trajectory planning for industrial robots | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b6f89528652c15379b9045ad126628673a47fb32/2-Figure1-1.png)

![ROS Q&A] 053 - How to Move a Robot to a Certain Point Using Twist - The Construct ROS Q&A] 053 - How to Move a Robot to a Certain Point Using Twist - The Construct](https://www.theconstructsim.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/ROS-QA-053-How-to-Move-a-Robot-to-a-Certain-Point-Using-Twist.png)




