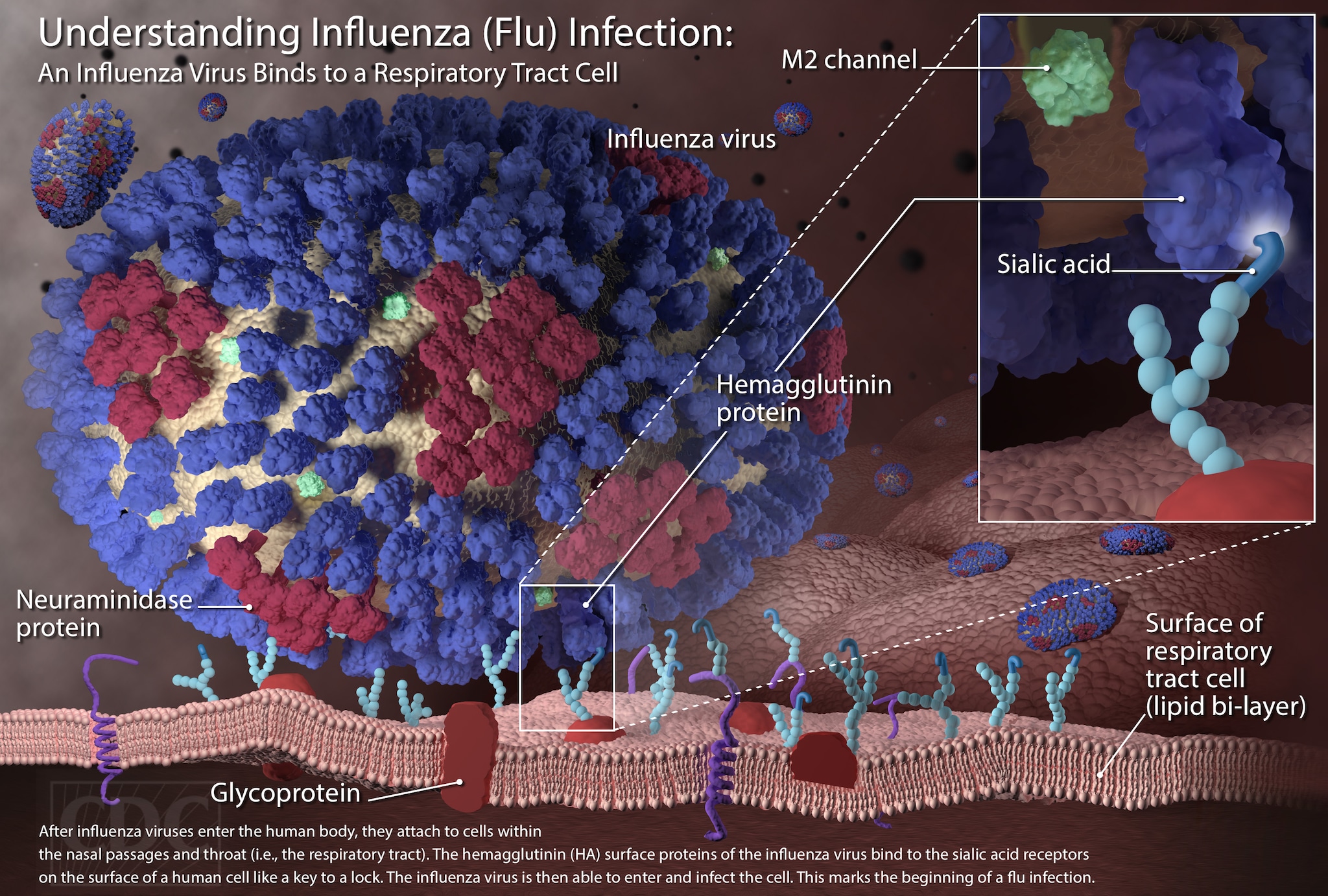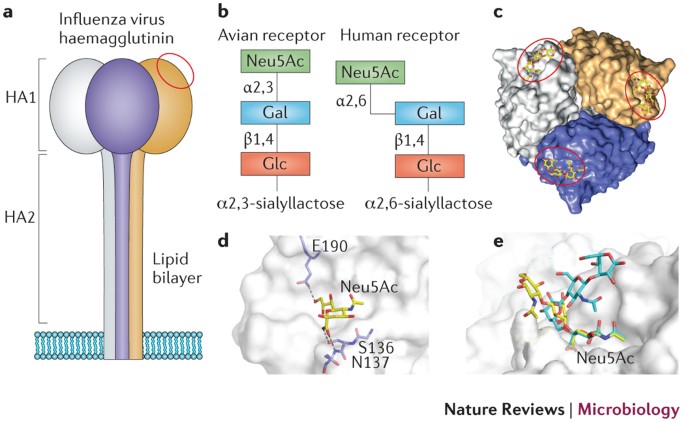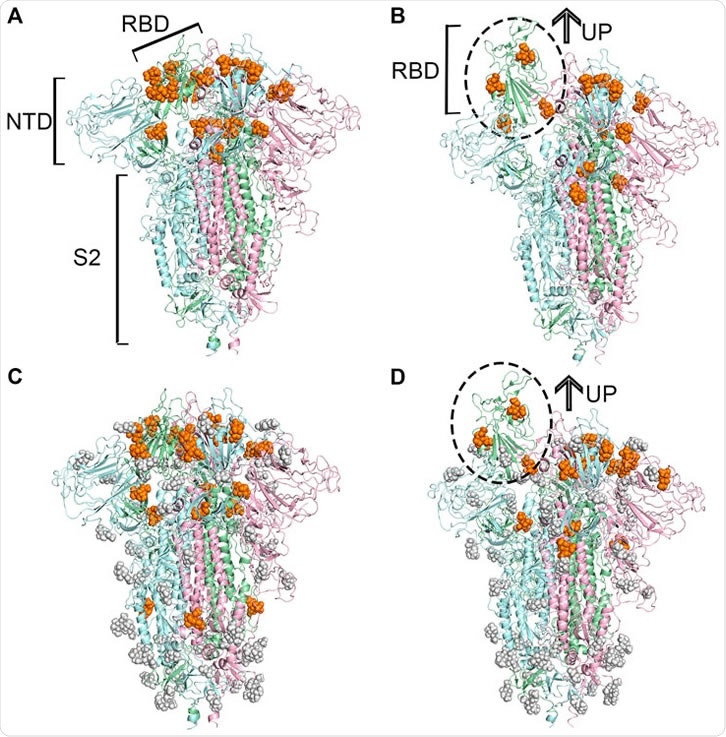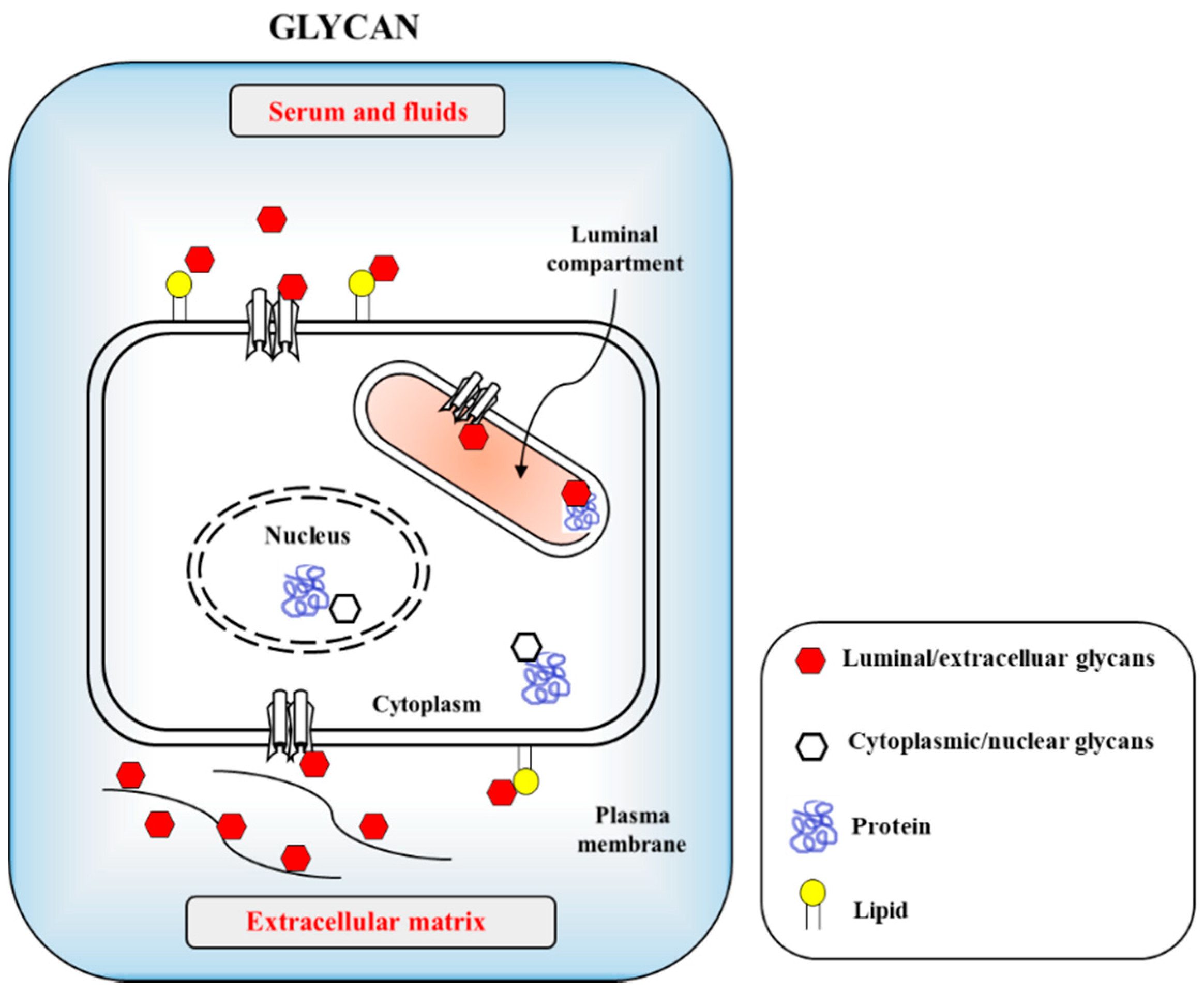
IJMS | Free Full-Text | SARS-CoV-2 Evolutionary Adaptation toward Host Entry and Recognition of Receptor O-Acetyl Sialylation in Virus–Host Interaction

Inhibitory Siglec-sialic acid interactions in balancing immunological activation and tolerance during viral infections - eBioMedicine

Glycosylation of Human IgA Directly Inhibits Influenza A and Other Sialic- Acid-Binding Viruses - ScienceDirect
The 2nd sialic acid-binding site of influenza A virus neuraminidase is an important determinant of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase-receptor balance | PLOS Pathogens

Identification of sialic acid-binding function for the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein | PNAS
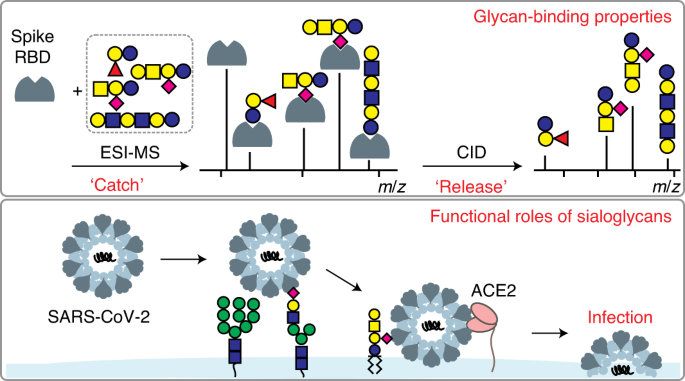
Sialic acid-containing glycolipids mediate binding and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2 | Nature Chemical Biology
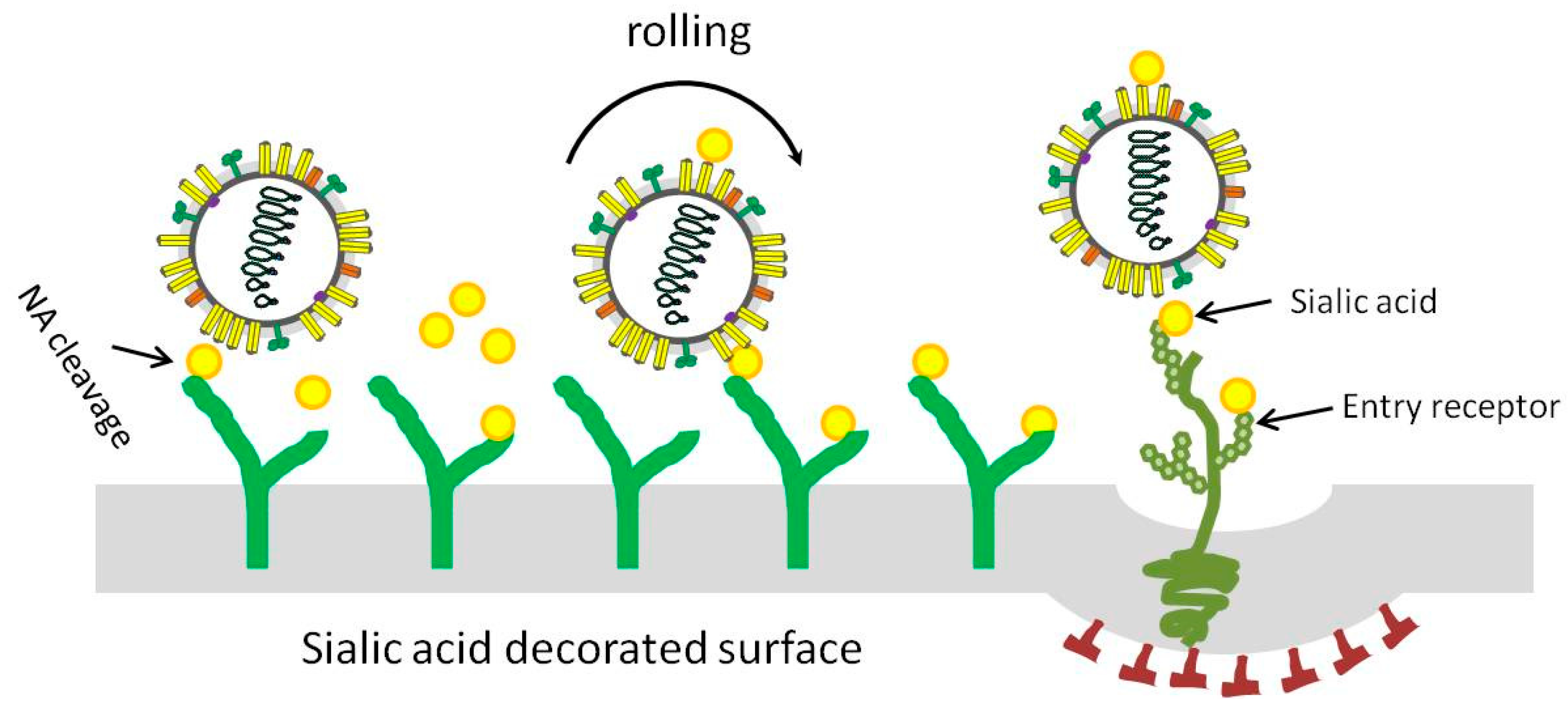
Viruses | Free Full-Text | Competitive Cooperation of Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase during Influenza A Virus Entry

Inhalation of α-gal/sialic acid liposomes: a novel approach for inhibition of influenza virus infection? | Future Virology
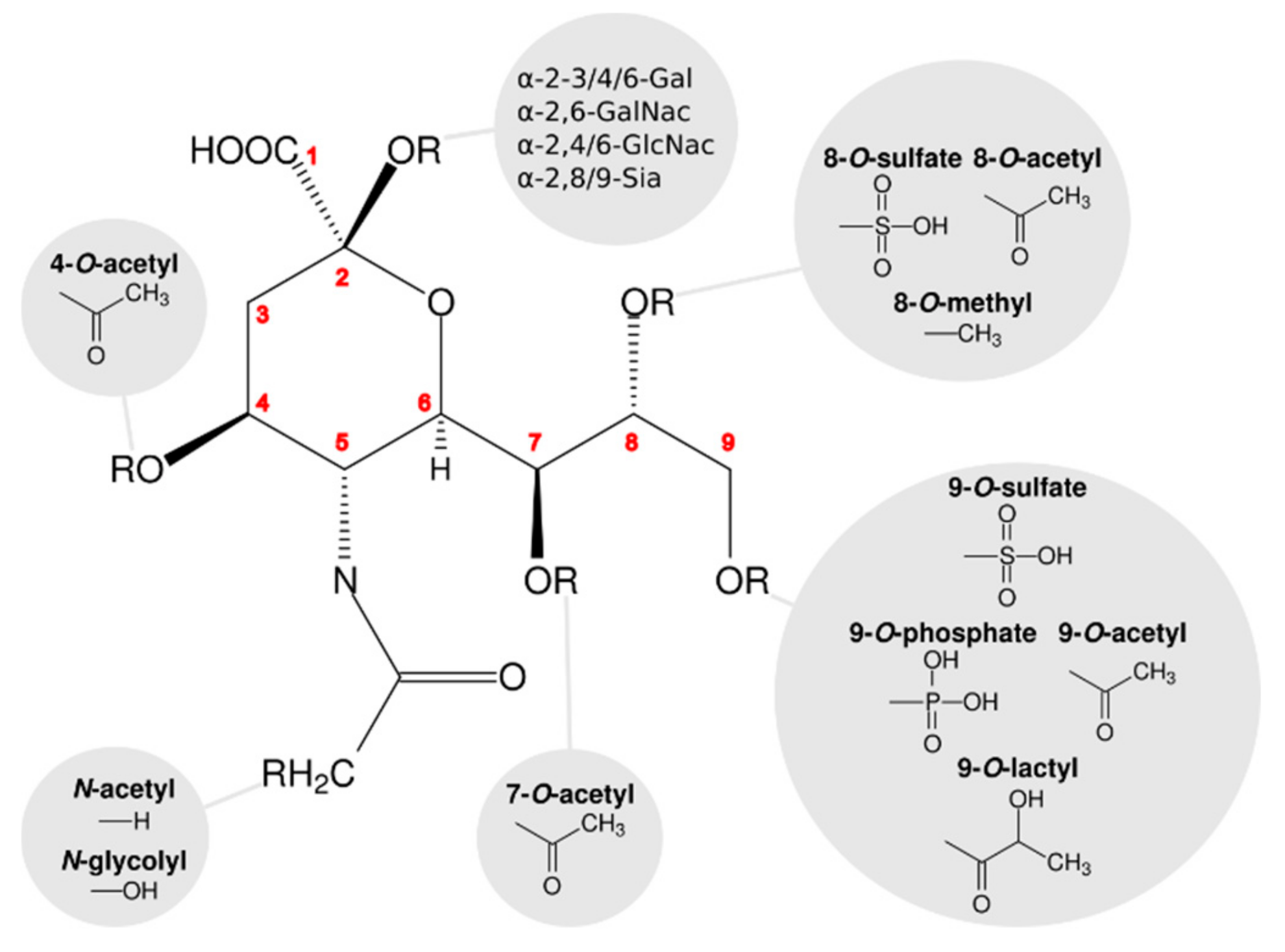
Viruses | Free Full-Text | The Symmetry of Viral Sialic Acid Binding Sites–Implications for Antiviral Strategies

Influenza A viruses use multivalent sialic acid clusters for cell binding and receptor activation | bioRxiv

Expression of 9-O- and 7,9-O-Acetyl Modified Sialic Acid in Cells and Their Effects on Influenza Viruses | mBio
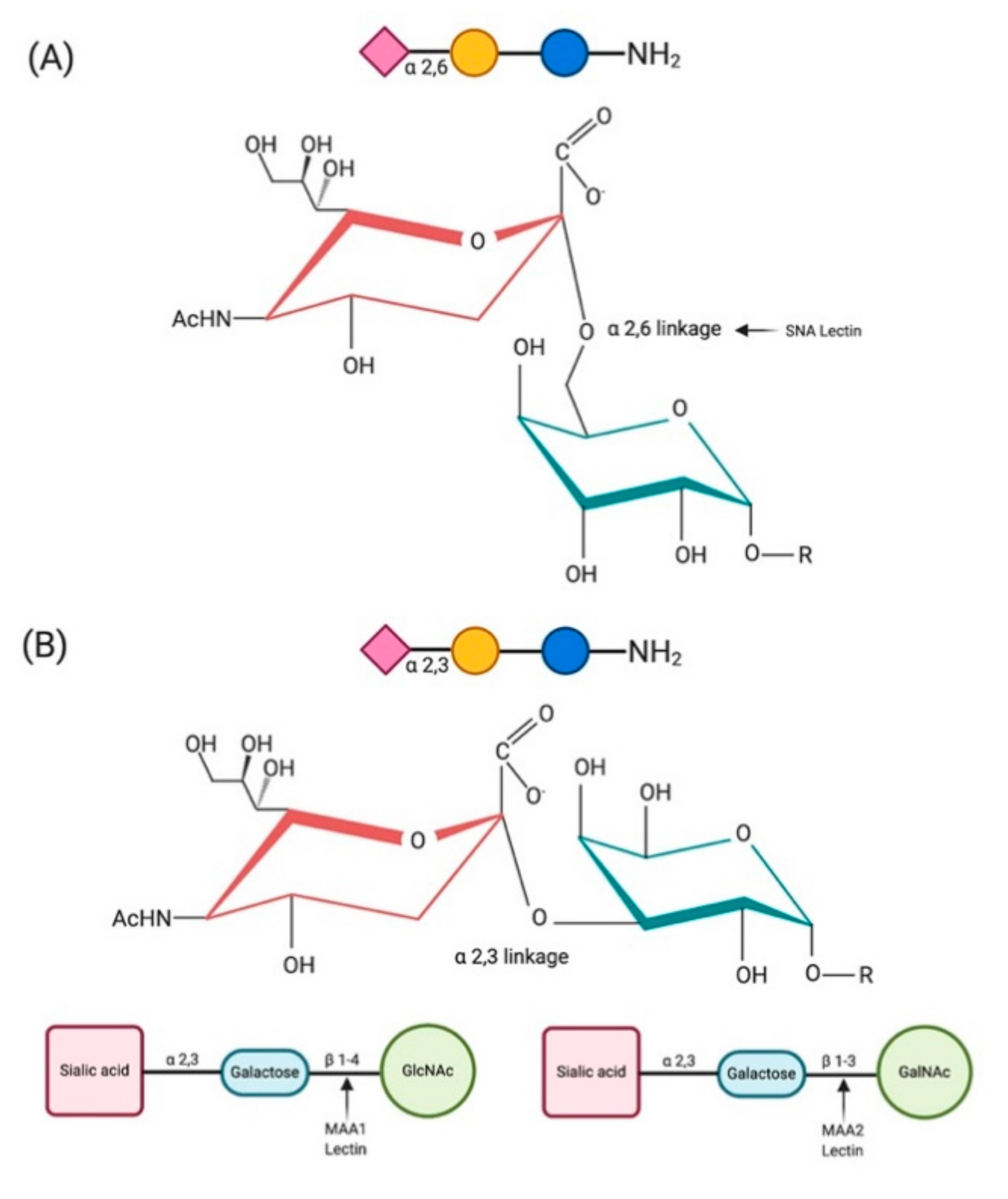
Viruses | Free Full-Text | Sialic Acid Receptors: The Key to Solving the Enigma of Zoonotic Virus Spillover

Avian influenza and sialic acid receptors: more than meets the eye? - The Lancet Infectious Diseases

A Sialylated Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channel Binds Hemagglutinin and Mediates Influenza A Virus Entry into Mammalian Cells - ScienceDirect

Sialic Acid-Mimic Peptides As Hemagglutinin Inhibitors for Anti-Influenza Therapy | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry

The SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein Binds Sialic Acids and Enables Rapid Detection in a Lateral Flow Point of Care Diagnostic Device | ACS Central Science
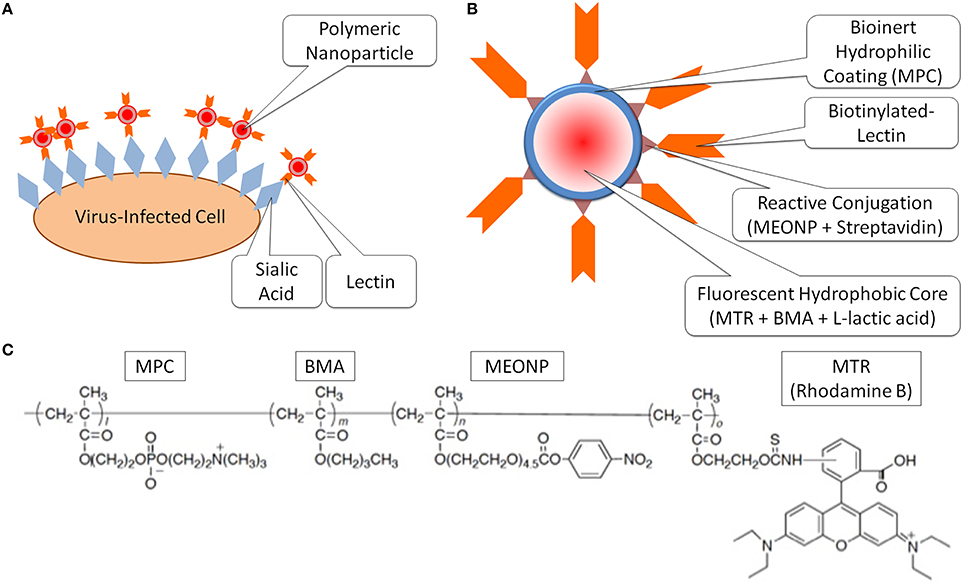
Frontiers | Analysis of the Changes in Expression Levels of Sialic Acid on Influenza-Virus-Infected Cells Using Lectin-Tagged Polymeric Nanoparticles

Influenza virus-induced lung injury: pathogenesis and implications for treatment | European Respiratory Society

Role of receptor binding specificity in influenza A virus transmission and pathogenesis | The EMBO Journal